Agreement between the state of NSW and Origin on its plans for Eraring power station
-
-
- Why we are upgrading our electricity system
- How we are transitioning our electricity system
- How NSW will benefit from the energy transition
-
- A long-term vision for locals
- The best office in the world
- The future of farming is here
- Renewables generates 100 new jobs for Western Sydney manufacturer
- The people behind NSW’s energy transition
- NSW ’s giant super battery is underway
- Unlocking opportunities for the people of Dubbo
- Meet Bridget from the Central-West Orana REZ
-
-
- Agreement between the state of NSW and Origin on its plans for Eraring power station
- NSW coal market price emergency
- Delivering a Gas Decarbonisation Roadmap
- NSW Embedded Network Action Plan
- NSW Transmission Planning Review 2025
- Network-to-network connection process
- Corrosion protection systems
- Demand response
- Electricity Market Operation Rules
-
- Review and reform
- Safeguard design
- Exemptions
-
-
-
- Air conditioner - eligibility
- Core eligibility
- Electric water heater replacement with a solar electric boosted water heater - eligibility
- Electric water heater replacement with an air source heat pump - eligibility
- Electric water heater replacement with an air source heat pump - eligibility
- Gas water heater replacement with a solar electric boosted water heater - eligibility
- Gas water heater replacement with an air source heat pump - eligibility
- Gas water heater replacement with an air source heat pump - eligibility
- HVAC - eligibility
- Heat pump water heater - eligibility
- Hot water heater - eligibility
- Install a new air source heat pump - eligibility
- Pool pump - eligibility
- Refrigerated cabinet - eligibility
- Solar battery - eligibility
- Solar battery - eligibility
- Solar battery eligibility landing
- Spare refrigerator or freezer - eligibility
- Ventilation or refrigeration motor - eligibility
-
- Air conditioner - certificates
- Electric water heater replacement with a solar electric boosted water heater - certificates
- Electric water heater replacement with an air source heat pump - certificates
- Electric water heater replacement with an air source heat pump - certificates
- Gas water heater replacement with a solar electric boosted water heater - certificates
- Gas water heater replacement with an air source heat pump - certificates
- Gas water heater replacement with an air source heat pump - certificates
- HVAC - certificates
- Heat pump water heater - certificates
- Hot water heater - certificates
- Install a new air source heat pump - certificates
- Pool pump - certificates
- Refrigerated cabinet - certificates
- Solar battery - certificates
- Solar battery certificates landing
- Spare refrigerator or freezer - certificates
- Ventilation or refrigeration motor - certificates
- Solar battery - certificates
-
-
- Administration and compliance
- Energy certificate schemes
- Gas network safety and operating plans
- Pipeline management plans
-
- Scaling up a thriving renewable fuel industry in NSW
- Going circular in clean energy
- Pipelines and Gas Supply Acts proposed updates - 2024
- Public consultation: Ministerial Statement of Expectations: Protecting NSW customers of embedded networks
- Solar emergency backstop
- ASP Scheme review
- Corrosion Protection Systems Regulation 2020
- Digital metering: improving service delivery in NSW
- Electricity Infrastructure Roadmap consultations
- Queensland-Hunter Gas Pipeline ATS
- Public lighting code
- Service and installation rules
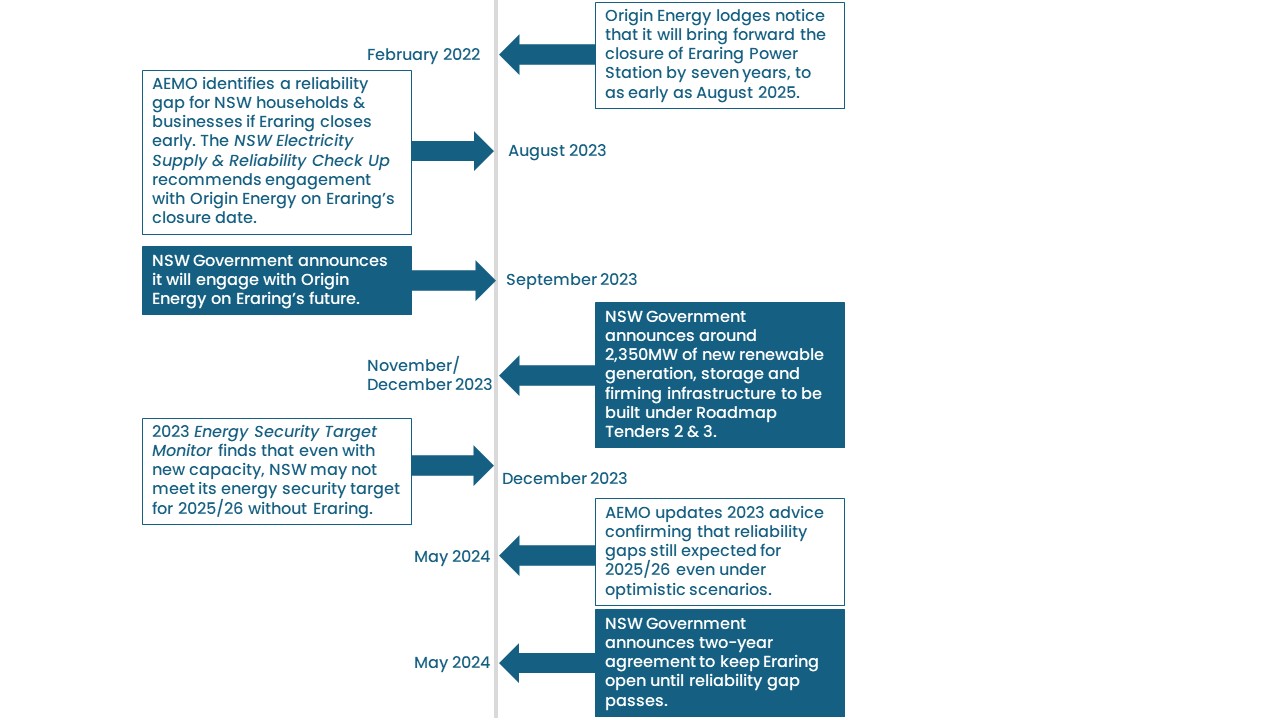
Eraring Power Station (Eraring) is NSW’s largest power station at 2880MW. It provides around 18 per cent of the State’s current electricity needs.
On 17 February 2022, the owner of Eraring – Origin Energy Limited (Origin) – gave notice it would close Eraring as early as August 2025. This is seven years earlier than previously expected.
In August 2023, the Australian Energy Market Operator released its annual Electricity Statement of Opportunities report, which found that a reliability gap would emerge in NSW from 2025/26 if Eraring closes in August 2025.
In September 2023, the NSW Government announced it would engage with Origin Energy on its plans for Eraring consistent with recommendations made in the NSW Electricity Supply and Reliability Check Up.
In November and December, the NSW Government announced NSW Electricity Infrastructure Roadmap tenders had resulted in support for around 2,350MW of new renewable generation, storage and firming infrastructure.
In December 2023, the Energy Security Target Monitor (ESTM) Report was released highlighting that additional actions may be necessary to ensure a reliable electricity supply following the scheduled retirement of Eraring power station in August 2025.
In May 2024, the Australian Energy Market Operator released an update to its 2023 Electricity Statement of Opportunities finding that despite the additional investment, there is a forecast reliability gap in NSW from 2025/26 if Eraring closes in August 2025.
On 23 May 2024, the NSW Government announced Origin had agreed to operate Eraring until August 2027 in return for Government underwriting against a share of its potential financial loss. If Origin accepts the underwrite, it is also required to pay a share of any profit to the Government. A summary of the agreement is available here.
On 4 June 2024, the Minister tabled the agreement with Origin in Parliament.
On 6 August 2024, the Minister tabled a summary of the evaluation of the agreement with Origin and related commercial advice and electricity modelling in Parliament.
The NSW Government has announced a suite of measures to support the transition to more affordable, reliable renewables and further reduce reliability risks, including:
- securing at least 2.2 of 6 gigawatts of renewable generation in the first National Tender under the Commonwealth Government's Capacity Investment Scheme.
- making 8 gigawatts of access rights available across the Central-West Orana and South West Renewable Energy Zones.
- introducing legislation to establish the Energy Security Corporation this year, with the plan to invest its $1 billion in seed funding in critical storage projects starting in 2025-26.
- providing $8.4 million in grants to Transgrid and AEMO to hire more engineers to fast-track connection of four major battery projects.
- expanding the Peak Demand Reduction Scheme to provide financial incentives for household batteries, which could take between $1,600 and $2,400 off the up-front cost.
- making it easier to get planning approval for wind, solar, and storage projects.
Timeline of NSW Government Eraring Update